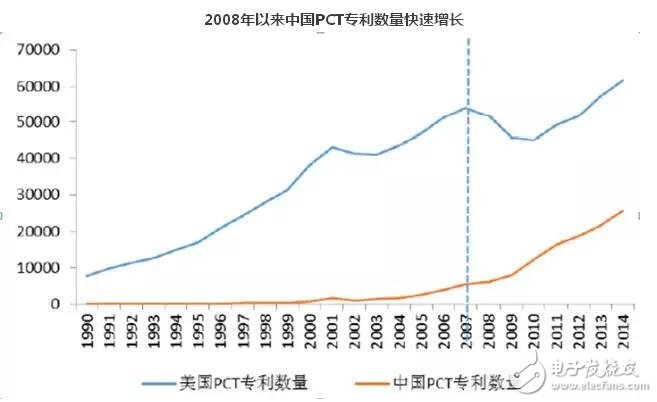
On November 18th, at the 3GPP meeting of the International Mobile Telecommunications Standardization Organization, the Polar code pushed by China was selected as the control channel coding scheme of the 5G eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) scenario. This is the first time that a Chinese company has entered the field of basic communication framework agreements, breaking Qualcomm’s long-standing monopoly on communication standards. The victory of the Polar code means the end of the Qualcomm monopoly era, and Huawei is making its debut with a strong figure. From the 3G in 1999, the 4G in 2009 to the 5G in 2016, it is the process of China's follow-up from communication to catching up and leading. In the past, China had almost no voice in the field of communication standards. All patented technologies in the 2G and 3G eras were monopolized by Qualcomm of the United States and Ericsson of Sweden, which directly caused China to remain in a passive position in the 2G, 3G and 4G eras. The disadvantages of being in a passive position are obvious. First, the security of key information systems faces enormous challenges. On the other hand, economic interests are directly damaged. The core technology of the information system is controlled by foreign giants, which makes Chinese manufacturers need to pay high patent licensing fees. For example, Qualcomm charges a 5% patent fee for 3G mobile phones sold in China and a 3.5% patent fee for 4G devices that do not implement CDMA or WCDMA network protocols. This ratio is not based on the chip price, but the whole machine. In this regard, Chinese mobile phone manufacturers contributed 53% of revenue to Qualcomm in fiscal 2015, totaling 25.28 billion US dollars, most of which are patent fees. According to statistics from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the average profit margin of China's mobile phone industry is only 3.2%. It can be said that the patent license fee paid to Qualcomm has taken away more than half of the profits of domestic mobile phones. a small step in the 5G Long March Although Huawei's main Polar code has been internationally recognized, Polar is only a small aspect of the 5G standard, and there are many aspects of technology to be standardized. Chinese companies still have a long way to go. The 5G standard is divided into two stages: coding and scheme. The coding is divided into three scenarios, namely mobile communication, Internet of Things and emergency communication. The eMBB corresponding to this Polar code belongs to the first scenario of the coding phase - high speed. The large-capacity mobile communication service needs to determine the coding of the other two scenarios before April 2017, and then enter the solution phase. Further, the selection of the code is only to determine the competition, and the choice of the program is more important. The plan is equivalent to the specific rules of the game and the detailed product manufacturing standards. After the project is selected, it will be approved by the ITU. The real standard is Counting the ground. However, Huawei has a patent advantage of 70% in the field of Polar code, and has a first-mover advantage. The probability of adopting the Huawei solution in the future is relatively high. Industrial Securities pointed out that the selection of this time is more of a dispute over the right to speak between technical routes, and the standard end is not so quickly transmitted to industrial applications. In the long run, the formation of a globally unified 5G standard can quickly promote the development of the entire industry chain and market. The selection of the Polar code is only a small part of this process. The 5G industry chain will not benefit and explode in advance. It is expected that 5G will be commercialized in 2019 or 2020. From technology follow-up to independent innovation After years of hard work, Chinese communication companies have gradually moved from technology to independent innovation, and the gap between them and international giants has gradually narrowed or even surpassed. The Polar code was not originally proposed by Huawei, but was from E. Arikan, a professor at the University of Birken in Turkey. However, Huawei, which values ​​its technical potential, has invested a lot of money in practical research. At present, the error correction performance that Polar code can achieve has exceeded the widely used. Turbo code and LDPC code. In the process of researching standards, promoters Huawei and Qualcomm will apply for relevant patents, and they also have first-mover advantages in technology and products. It is understood that Huawei's core patents in the Polar standard account for 70%, and Qualcomm also occupies most of the patents related to LDPC. In the future, once commercial products and solutions use related patents, Huawei and Qualcomm can collect corresponding patent fees. The two companies at the top of the industry chain will undoubtedly draw the most lucrative profits. From the perspective of Huawei's development process, it initially occupied the market mainly by absorbing and digesting foreign technology and taking advantage of the cost advantage brought by the engineer's human dividend. In the process, it also experienced the lack of core technology, and suffered from the painstaking payment of high patent license fees after patent litigation with companies such as Cisco and Qualcomm. However, despite this, Huawei still maintains a large amount of R&D investment for many years. The proportion of R&D in revenue has increased from 10% in the previous period to 14.2% in 2015, close to 60 billion yuan, far exceeding the industry level, ranking ninth in the world. . According to Yu Chengdong, CEO of Huawei's consumer business, Huawei's R&D investment is expected to become the world's number one in the foreseeable two or three years. Long-term high R&D investment has caused Huawei to gradually break the monopoly of the giant technology on the core technology, and has the enthusiasm of enterprises such as Qualcomm. At present, Huawei's core technology, in addition to the well-known Hess Kirin chips, also involves servers, storage technologies, cloud computing operating systems, high-capacity data center switches, next-generation WIFI technology, and 4G and 5G technologies. The official research of the Polar code is only 4 years, and it has defeated the LDPC code of more than 50 years in the control channel eMBB scene coding scheme, which also proves its strong R&D capability. So far, Huawei has established 16 R&D centers and 36 joint innovation centers in China, Germany, Sweden, Russia and India, with more than 170,000 employees and 50,377 patents worldwide. According to the announcement issued by the World Intellectual Property Organization in March 2016, Huawei ranked No. 3,389 patents for the second consecutive year in the corporate world, and ranked second in the Qualcomm and ZTE, and the number of patents applied for by the “Runner†Qualcomm was only 2,442. As a representative of China's scientific and technological community, Huawei's development process is the epitome of the development of China's science and technology industry - from the initial technology follow-up to the gradual replacement of domestic technology to technological innovation. Other communication companies are also replicating Huawei's development path: initially taking advantage of cost advantages to occupy the market, and then strengthening R&D investment, from focusing on marketing to R&D, and then achieving partial breakthroughs in independent innovation and core technologies. OPPO, which has always been a "marketing master" image, also has an unknown side - OPPO has publicly applied for 3,338 patents in 2015, ranking fourth in the ranking of corporate invention patent applications received by the National Intellectual Property in 2015. After ZTE. Huawei's old rival ZTE also continued to increase R&D investment. Its R&D investment in the first half of 2016 also closed to the historical high of 15% for the first time, reaching 7.059 billion yuan. The establishment of Xiaomi, which was only 6 years old, was blocked in the international market due to patent problems. It also increased patent investment. In 2015, the number of patent applications received reached 3,183, ranking sixth. At present, the independent innovation of domestic mobile phone manufacturers is mainly reflected in the adjustment of hardware details such as mobile phone screen, shell material and sensors. For example, Xiaomi has released a curved screen, Note2 with 3D glass body and Xiaomi MIX with full screen. OPPO has introduced flash charging. Technology and image chip anti-shake technology. In terms of core technology, Xiaomi has tried to independently develop chips to reduce the cost of the whole machine. However, the accumulation of core technologies can not be achieved in a short period of time. Xiaomi has not achieved remarkable results yet, and the red rice 2A using the independent processor is only a short-lived one. On the whole, according to the report of the World Intellectual Property Organization, although the United States is still the country with the largest number of patent applications, China is the fastest growing country. In 2015, a total of 29,800 patents were submitted. Currently, the number of patent applications is only Second in the United States and Japan, ranking third in the world. From the trend of the number of PCT patents in China and the United States, the number of patents in China has accelerated after 2008, and the effect of China's technology industry from absorption and application to innovation has begun to appear (with photos). From the technical field, digital communications and computer technology submitted the most patent applications in 2015, both exceeding 16,000, accounting for about 8% of the total number of applications, followed by electronics, machinery and medical technology. The top three companies in the number of patent applications are from the digital communications field, and because the patent barriers in the communications industry are serious, no patents are equivalent to being shackled. RF Connector,PCB Mount,Angled/90° Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.yiucn.com